The following article aims to explore the impact of Covid-19 on the tourism industry worldwide. This includes the effects of the pandemic, the risks involved for travelers, and the measures taken by governments across the world. The data has been collected through various trusted sources. The findings reveal how the countries dependent on tourism were affected the most. It gives an insight into the pace of recovery in the days to come.
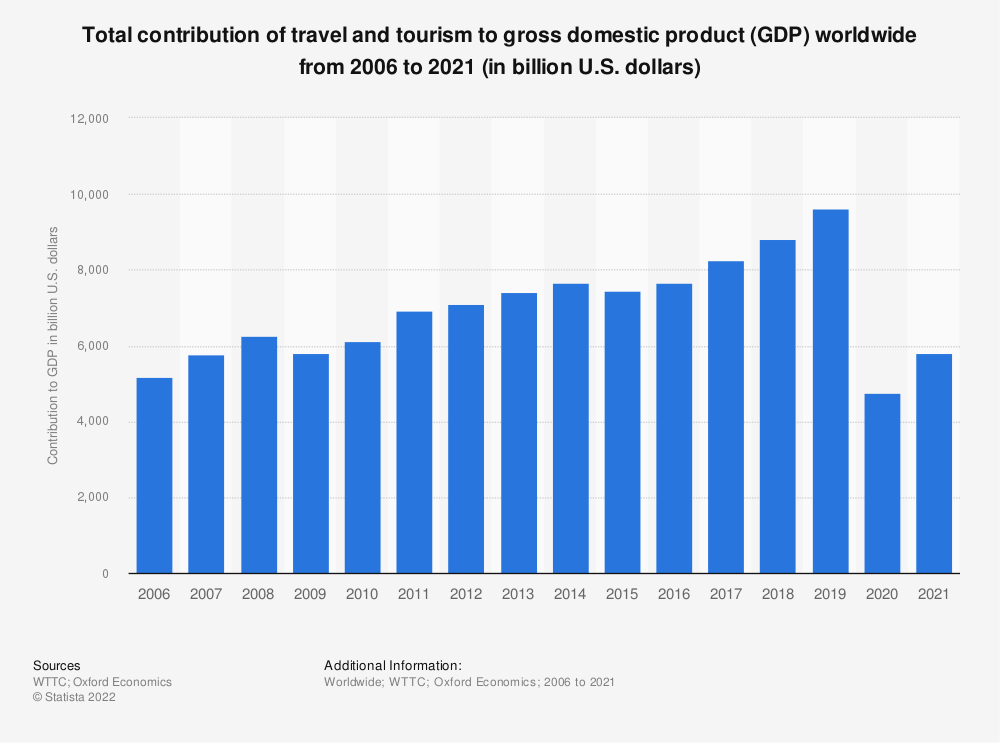
Since 1980, the tourism industry has seen unprecedented growth from 277 million to nearly 1.5 billion in 2019. Despite minor bumps like the SARS epidemic of 2003 and the global financial crisis of 2009, tourism was a thriving industry until the COVID-19 pandemic drastically hit it.
The tourism industry, a strategic pillar of economic growth for countries worldwide, took a major blow with the onset of the pandemic and has been on the road to recovery since.
According to reports, international and domestic tourism experienced a 4% upturn in 2021, with 15 million more tourist arrivals than in 2020; they were still 72% below the pre-pandemic year of 2019. 2020 has been the worst year on record for tourism when international arrivals decreased by 73%. Globally, travel and tourism are significant contributors to job creation.
Moreover, it plays an important role in socio-economic and cultural development too. Today, tourism has become the most vulnerable industry of being the hub of leisure, economic activities, and customer satisfaction. According to experts, the worldwide tourism industry is not expected to recover to 2019 levels until 2023.
Tourism dependent industries impacted by the Pandemic
In 2020, travel plans worldwide went down by 80–90% due to various restrictions and borders closed. Many tourist attractions worldwide, such as museums, amusement parks, and sports venues, closed down due to travel restrictions imposed regionally. A 65% drop in international tourist arrivals was reported in the first six months of 2020.
The sectors most impacted were
- Air – Air passenger travel showed a huge decline during the pandemic, with most borders closed.
- Casinos – Casinos around the world took a hit due to low footfall.
- Cruise – Cruise liners had to cancel sailings after the pandemic outbreak, and many passengers got infected onboard.
- Hotel industry – This was the worst hit, with most rooms going vacant as people wouldn’t step out due to travel restrictions.
- Rental car industry – Car rentals were declining due to a smaller number of travelers.
- Restaurants – The spread of the virus affected restaurants across the world.
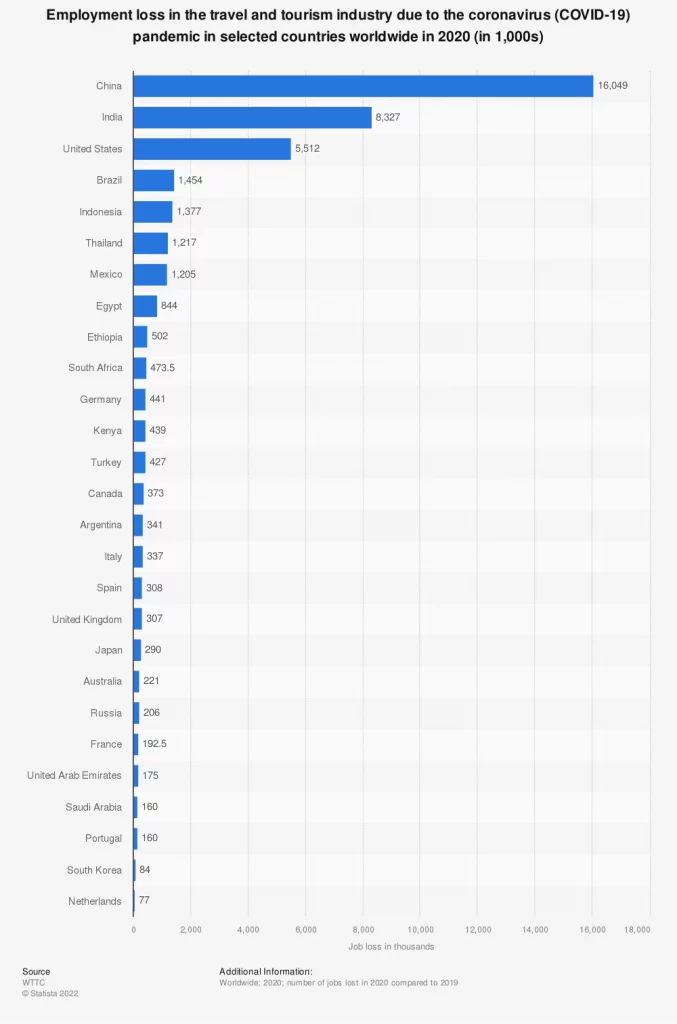
Tourism is one of the deeply impacted industries due to its dependency on the human factor. Even today, some companies are still struggling with the labor shortage as many have switched jobs in a crisis. The impact of the pandemic was particularly felt in countries where tourism is an important part of economic growth. Tourism as a sector has taken the brunt of serious damage worldwide.
Post pandemic bounce back – Measures taken across countries to push the plug.
Though the road to recovery will not be a smooth sail, some countries are witnessing a bounce back. With improvement in vaccination rates, the pace of recovery is moving in a positive direction. A rebound can be seen from the second half of 2021 due to the opening of borders for many countries. However, most experts expect a full recovery by 2024 or later. More precisely, international and domestic tourism will return to pre-pandemic levels in 2023.
Rise in domestic travel – discovering one’s own country
The World Tourism and Travel Council have reported that there has been a shift after the pandemic, where travelers are focusing on domestic trips or nature and outdoor destinations. Tourists are largely opting for less risky travel destinations, from adventure travelling and backpacking to surfing and mountain climbing are some of the latest travel trends. The governments of tourism-dependent nations are developing global protocols for various travel industries, including more rapid testing at airports to boost travel confidence. Following necessary protocols to give travelers the much-needed assurance of safety. Leisure and business travel is making a comeback in the tourism and travel sector; this can be a crucial source of revenue for hotels and airlines.
In a new era of remote work, across countries, more and more people are opting for domestic travelling for long stays away from home, mixing work with pleasure. Staycations are also gaining huge popularity in boosting domestic tourism. In the era of the new normal, tourist behavior is also drifting towards health first. People are travelling cautiously with more awareness by following all the required safety protocols. This, too, is impacting the resumption and recovery of domestic and international tourism. Most households now have more money available to spend on travel, thanks to the savings accrued during a pandemic, in which there was almost no money spent on leisure. This has given rise to revenge travelling, where people now want to travel even more than before to cover the lost time when they were in complete lockdown.
For Tourism-dependent countries, the negative impact of the crisis would stay much longer than in other economies.
Among tourism-dependent economies, evidence suggests that those relying more heavily on international tourism experienced a more severe hit to economic activity than those relying more on domestic tourism. The pace of recovery will remain slow and uneven, especially for economies heavily dependent on tourism.
A country like Seychelles, which had experienced an offset in tourism, has benefited from increased tuna exports during the COVID-19 period, although these earnings remain a fraction of tourism receipts. The government jotted a plan to pay wages to displaced tourism-sector workers while offering opportunities for retraining. The Maldives is another country dependent mostly on tourism, which has reopened by slashing rates of most luxury resorts to attract travelers.
Countries like Thailand now admit tourists from “low-risk” countries with special quarantine requirements. Italy and Spain remain the worst countries for the coronavirus pandemic. In the Philippines, job losses and a decrease in average working hours in 2020 were among the highest. In Viet Nam, nearly one-third of total job losses were linked to the tourism sector. Fiji, a popular destination in the South Pacific, saw an overall economic decline of 21.7 per cent. The Bahamas, a favorite destination among cruise-goers, reopened after a long haul with various restrictions, like asking the guests to remain on property at their resort or hotel.
Conclusion
The outlook for international and domestic tourism in 2022 looks promising, especially with increasing vaccine coverage and travel protocols. Still, a complete recovery is a distant dream for many countries, particularly for smaller tourist destinations; it remains a daunting challenge.
Also Read:





